Modern Mole Removal: What to Know About Methods and Expectations
Many people explore modern mole removal to improve skin appearance or for comfort. While methods may vary, there are non-invasive and clinical options that people consider based on their needs. Learn what to expect, how others approach it, and what influences the choice. Learn more inside.
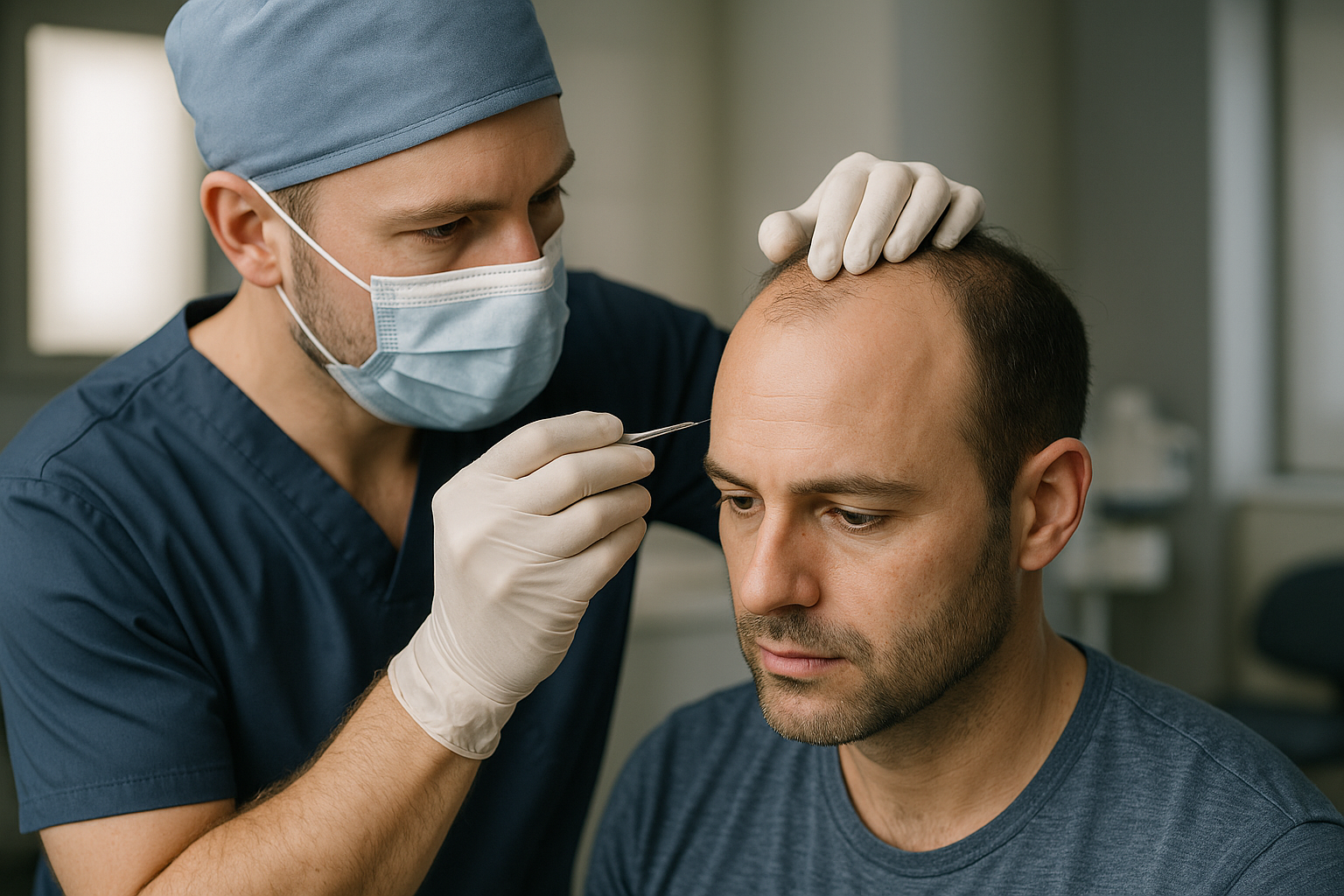
What Are the Different Modern Mole Removal Methods Available?
Modern mole removal methods have evolved considerably, offering patients various options depending on their specific needs. Clinical mole removal procedures include surgical excision, where the mole and surrounding tissue are completely removed with a scalpel. Shave excision involves removing the mole at skin level using a surgical blade, typically for raised moles. Laser removal uses focused light energy to break down mole tissue, though this method works best on smaller, non-cancerous moles.
Cryotherapy represents another clinical approach, using liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy mole tissue. Electrosurgery combines electrical current with surgical removal, offering precision for specific mole types. Each method has distinct advantages depending on the mole’s size, location, and characteristics.
How to Remove Moles Safely Without Complications?
Safe mole removal begins with professional medical evaluation. Dermatologists assess moles for signs of irregularity, asymmetry, border changes, color variations, or diameter changes that might indicate potential health concerns. This evaluation determines the most appropriate removal method and ensures safety throughout the process.
Proper aftercare plays a crucial role in safe healing. Following medical instructions for wound care, avoiding sun exposure on treated areas, and monitoring for signs of infection help prevent complications. Professional removal significantly reduces risks compared to attempting home removal methods, which can lead to scarring, infection, or incomplete removal.
Are Non-Invasive Mole Removal Options Effective?
Non-invasive mole removal options include laser therapy and certain topical treatments prescribed by dermatologists. Laser removal works effectively for specific types of moles, particularly smaller, flat moles without deep root systems. The procedure typically requires multiple sessions and works by breaking down pigmented cells gradually.
However, effectiveness varies considerably based on mole characteristics. Raised moles or those with deeper tissue involvement may not respond well to non-invasive methods. Some moles may require traditional surgical removal for complete elimination. Dermatologists evaluate each case individually to determine whether non-invasive options will achieve desired results.
What Should You Expect During Clinical Mole Removal Procedures?
Clinical mole removal procedures typically begin with local anesthesia to ensure patient comfort. The dermatologist explains the chosen method and expected outcomes before beginning treatment. Surgical excision involves making an incision around the mole, removing it completely, and closing the area with sutures when necessary.
Recovery time varies by procedure type and location. Surgical removal may require 1-2 weeks for initial healing, while laser treatments often have shorter recovery periods. Patients can expect some discomfort, possible swelling, and temporary skin discoloration. Follow-up appointments ensure proper healing and address any concerns that arise during recovery.
What Unique Considerations Apply to Mole Removal in America?
In the United States, mole removal practices emphasize comprehensive skin cancer screening alongside cosmetic concerns. American dermatologists frequently recommend annual skin examinations, particularly for individuals with multiple moles or family history of skin cancer. This preventive approach often identifies concerning moles before they become problematic.
Insurance coverage varies significantly across American healthcare systems. Medical mole removal for health reasons typically receives coverage, while purely cosmetic removal may require out-of-pocket payment. Many dermatology practices offer payment plans or financing options to make treatment accessible. The abundance of qualified dermatologists across the country provides patients with multiple options for finding appropriate care in their local area.
What to Expect From Mole Removal Costs and Provider Options?
Mole removal costs in the United States vary considerably based on removal method, mole size, location, and geographic region. Understanding typical pricing helps patients plan appropriately for treatment.
| Procedure Type | Typical Cost Range | Recovery Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Excision | $150-$500 per mole | 1-2 weeks | Large, suspicious, or deep moles |
| Shave Excision | $100-$300 per mole | 5-10 days | Raised, benign moles |
| Laser Removal | $200-$600 per session | 3-7 days | Small, flat, cosmetic moles |
| Cryotherapy | $75-$200 per mole | 1-2 weeks | Small, benign surface moles |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Insurance typically covers medically necessary mole removal when performed by dermatologists, but cosmetic removal usually requires self-pay. Many practices offer consultation fees ranging from $100-$300, which may be applied toward treatment costs. Geographic location significantly impacts pricing, with urban areas generally commanding higher fees than rural regions.
Mole removal represents a common dermatological procedure with multiple effective approaches available. Whether seeking removal for medical or cosmetic reasons, consulting with qualified dermatologists ensures appropriate treatment selection and optimal outcomes. Understanding available methods, safety considerations, and realistic expectations helps patients make informed decisions about addressing unwanted moles while prioritizing their health and satisfaction with results.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




