Mechanic Training in Warsaw – Learning Structure and Technical Essentials
In Warsaw, mechanic training usually follows a clear sequence designed to help learners understand how mechanical systems work and how basic diagnostic practices are applied. Individuals who speak English can explore the typical learning environment, which often combines theoretical explanations with practical demonstrations, safe tool handling and routine maintenance exercises. These steps contribute to a steady learning rhythm that supports comprehension and consistency. This overview describes how mechanic training is generally organised in Warsaw without implying commitments or professional opportunities.
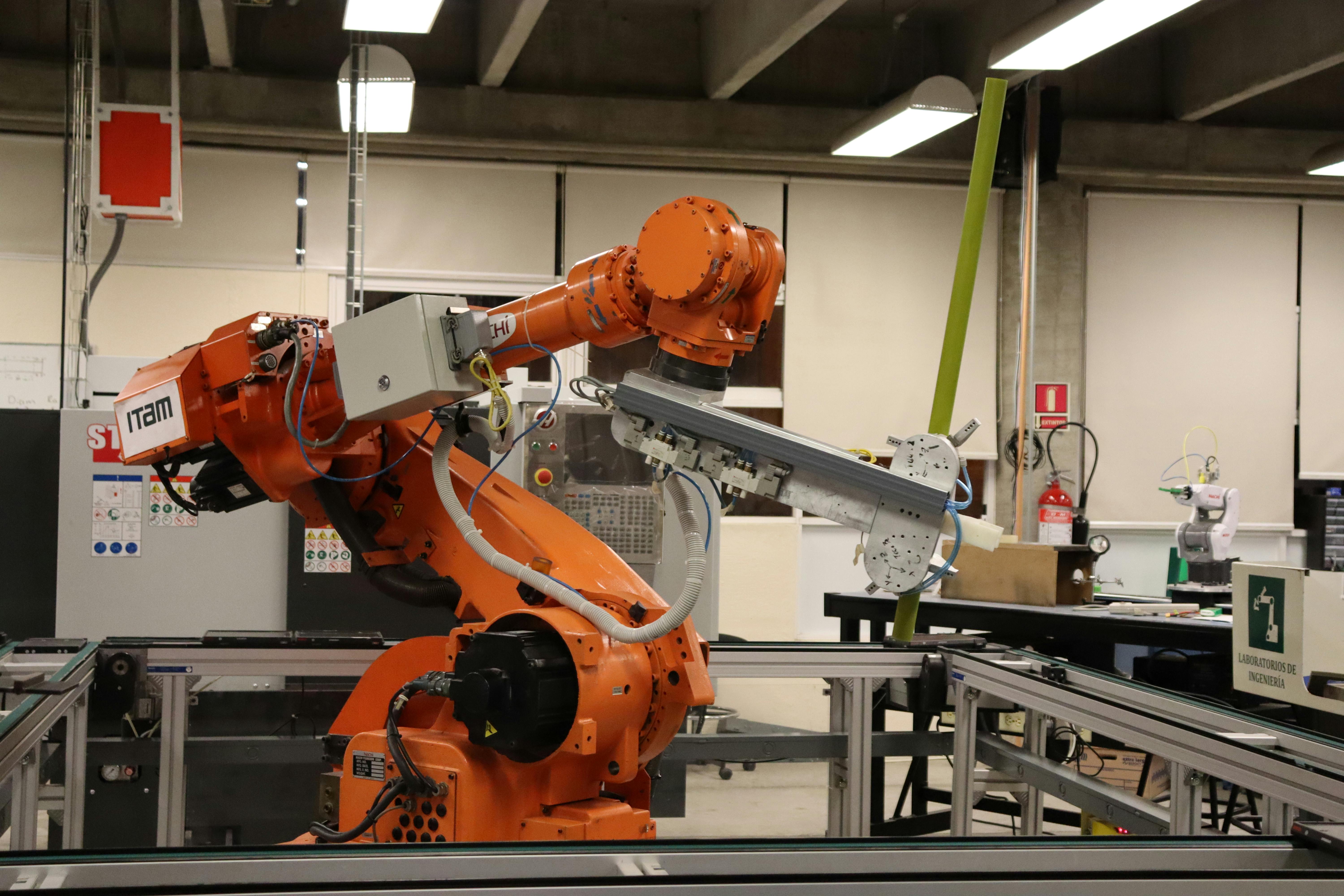
Mechanical engineering training programs in Warsaw provide a solid foundation for individuals seeking to develop expertise in designing, analyzing, and maintaining mechanical systems. These programs are designed to equip students with both theoretical understanding and practical skills necessary for success in various industrial applications. The curriculum typically spans several semesters and incorporates classroom instruction, laboratory work, and real-world project experience.
What Are Mechanical System Basics?
Mechanical system basics form the cornerstone of any engineering training program. Students begin by learning fundamental principles of physics, including mechanics, thermodynamics, and fluid dynamics. These concepts are essential for understanding how machines operate and how energy transfers within mechanical systems. Core topics include statics and dynamics, material science, and the behavior of solids under stress. Training programs in Warsaw emphasize mathematical modeling and problem-solving techniques that allow future engineers to analyze complex systems. Students also study computer-aided design software, which has become indispensable in modern engineering practice. Understanding these foundational elements enables trainees to progress toward more specialized areas of mechanical engineering.
How Does a Structured Learning Path Work?
A structured learning path in mechanical engineering training follows a progressive sequence designed to build competency systematically. Initial coursework focuses on mathematics, including calculus, differential equations, and linear algebra, which serve as tools for engineering analysis. As students advance, they encounter subjects such as machine design, control systems, and manufacturing processes. The curriculum typically integrates laboratory sessions where students apply theoretical concepts to tangible problems. Project-based learning allows participants to work in teams, simulating real workplace environments. Many programs in Warsaw also incorporate internship opportunities with local industries, providing exposure to professional settings. This structured approach ensures that graduates possess both depth and breadth of knowledge, making them competitive in the job market.
What Role Do Practical Demonstrations Play?
Practical demonstrations are integral to mechanical engineering education, bridging the gap between theory and application. Training facilities in Warsaw often feature well-equipped workshops and laboratories where students can interact with machinery, tools, and testing equipment. Demonstrations typically cover topics such as machining operations, welding techniques, assembly procedures, and quality control methods. Instructors guide students through step-by-step processes, highlighting best practices and common pitfalls. Hands-on sessions allow learners to develop manual dexterity and technical intuition that cannot be gained through textbooks alone. Practical work also fosters critical thinking, as students must troubleshoot problems and optimize solutions in real time. This experiential learning component is highly valued by employers who seek candidates with proven practical competencies.
Why Are Safe Handling Techniques Important?
Safe handling techniques are paramount in mechanical engineering training due to the inherent risks associated with operating machinery and working with materials. Programs in Warsaw place strong emphasis on workplace safety, teaching students to identify hazards, use personal protective equipment, and follow established safety protocols. Training includes instruction on proper use of hand tools, power tools, and industrial equipment. Students learn about lockout-tagout procedures, emergency response, and hazard communication standards. Understanding material safety data sheets and chemical handling procedures is also part of the curriculum. By instilling a safety-first mindset early in their education, training programs prepare students to contribute to safer work environments throughout their careers. Compliance with international safety standards ensures that graduates can work in diverse industrial settings globally.
What Does a Technical Overview of Training Include?
A technical overview of mechanical engineering training encompasses the full spectrum of knowledge and skills imparted during the program. Core engineering sciences include mechanics of materials, heat transfer, and machine elements. Students study power generation and transmission systems, including internal combustion engines, turbines, and hydraulic systems. Advanced topics may cover robotics, automation, finite element analysis, and computational fluid dynamics. Training programs in Warsaw often tailor their curricula to meet regional industry needs, with some emphasizing automotive engineering while others focus on manufacturing or energy systems. Assessment methods typically include written examinations, practical tests, project presentations, and capstone design projects. Graduates emerge with comprehensive technical competencies that prepare them for professional certification and licensure processes.
How Do Training Costs Compare?
The cost of mechanical engineering training in Warsaw varies depending on the institution, program duration, and level of study. Public universities generally offer more affordable tuition compared to private institutions, though both provide quality education. Full-time undergraduate programs typically span four to five years, while specialized technical courses may range from several months to two years. Additional expenses include textbooks, laboratory fees, software licenses, and materials for projects. Some institutions offer scholarship opportunities or financial aid packages to support students. International students should also consider accommodation, living expenses, and visa-related costs when budgeting for their education.
| Program Type | Institution Example | Duration | Estimated Annual Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree | Public Technical University | 4 years | €1,000 - €2,500 |
| Vocational Training | Technical College | 2 years | €800 - €1,800 |
| Specialized Course | Private Training Center | 6-12 months | €1,500 - €3,500 |
| Master’s Degree | Public University | 2 years | €1,200 - €3,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Conclusion
Mechanical engineering training in Warsaw offers a comprehensive educational experience that prepares students for successful careers in diverse technical fields. Through structured learning paths, practical demonstrations, and emphasis on safety, these programs develop well-rounded professionals capable of addressing complex engineering challenges. Understanding the curriculum structure, hands-on components, and financial considerations helps prospective students choose the right program for their career goals. As Poland continues to develop its industrial and technological sectors, the demand for skilled mechanical engineers remains strong, making this an opportune time to pursue training in this field.




