France – Medical Assistant Training For English Speakers Overview
In France, English speakers can gain an understanding of the medical assistant sector through general training programs. These programs provide insights into clinical procedures, administrative tasks, and patient interaction processes, offering a comprehensive view of the field. This overview highlights common practices, workflows, and organizational routines within medical facilities across France, giving readers information about how the industry operates without referencing specific jobs.
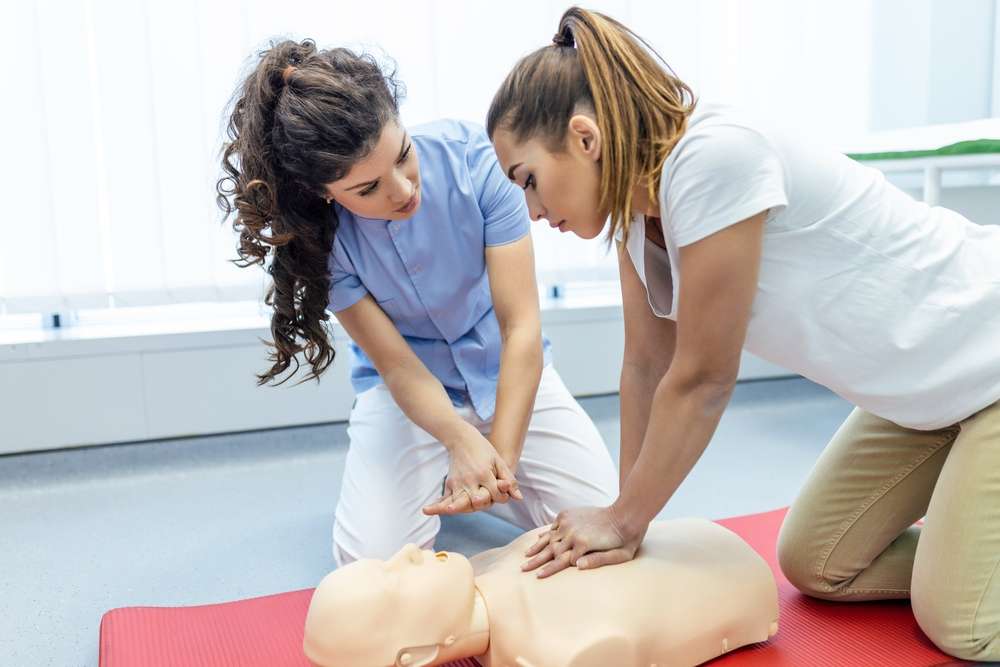
Medical assistant training in France provides comprehensive preparation for individuals seeking to support physicians, nurses, and healthcare teams in various clinical settings. The role combines hands-on patient care with administrative responsibilities, requiring both technical competence and organizational skills. For English speakers navigating the French healthcare education system, understanding program structures, language requirements, and career pathways becomes essential for successful entry into this field.
What Does Medical Assistant Training in France Include
Medical assistant training programs in France typically cover fundamental clinical procedures, patient interaction protocols, and healthcare facility operations. Students learn vital sign measurement, basic laboratory techniques, medical terminology, and patient documentation practices. The curriculum emphasizes infection control, medical equipment sterilization, and emergency response procedures. Training also addresses ethical considerations, patient confidentiality regulations, and professional communication standards within French healthcare environments. Most programs require proficiency in French medical terminology, though some international institutions offer bilingual or English-language foundational courses before transitioning to French-language clinical training.
Clinical Procedures Overview for Medical Assistants
Clinical procedures form the practical foundation of medical assistant responsibilities. Training covers blood pressure monitoring, temperature assessment, pulse measurement, and respiratory rate evaluation. Students practice venipuncture techniques, specimen collection, and basic laboratory sample preparation. Wound care fundamentals, including dressing changes and bandaging techniques, receive significant attention. Programs teach electrocardiogram administration, injection techniques for various medications, and proper handling of medical instruments. Practical sessions simulate real healthcare environments, allowing students to develop competence before entering clinical placements. Understanding French healthcare protocols ensures medical assistants can function effectively within established institutional frameworks.
Patient Care Practices in French Healthcare Settings
Patient care practices emphasize dignity, safety, and effective communication throughout all interactions. Medical assistants learn proper patient positioning for examinations, assistance with mobility and transfers, and comfort measures during procedures. Training addresses cultural sensitivity, particularly important in France’s diverse healthcare environment serving multiple communities. Students develop skills in patient education, explaining procedures in accessible language, and providing post-visit instructions. Documentation practices follow strict French healthcare regulations, requiring accurate record-keeping and timely information updates. Medical assistants also coordinate between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring smooth communication flow and appointment management.
Administrative Workflows in Healthcare Organizations
Administrative workflows constitute a significant portion of medical assistant responsibilities in French healthcare facilities. Training covers appointment scheduling systems, patient registration procedures, and insurance verification processes specific to France’s healthcare coverage system. Students learn electronic health record management, medical coding basics, and billing procedures aligned with French healthcare reimbursement structures. Telephone etiquette, reception management, and patient inquiry handling receive practical emphasis. Understanding France’s Carte Vitale system and complementary insurance arrangements becomes essential for efficient administrative operations. Medical assistants also manage supply inventory, equipment maintenance scheduling, and coordination with external laboratories and specialists.
Healthcare Organization and Professional Integration
Healthcare organization training prepares medical assistants to function within France’s structured medical environment. Students learn hospital departmental structures, clinic operational hierarchies, and interdisciplinary team collaboration. Training addresses quality assurance protocols, safety reporting systems, and continuous improvement practices. Professional development components cover career advancement pathways, continuing education requirements, and specialization opportunities within medical assisting. Understanding French labor regulations, workplace rights, and professional associations helps graduates navigate employment successfully. Integration into French healthcare teams requires adaptability, ongoing language development, and commitment to evidence-based practices aligned with national healthcare standards.
Training Costs and Program Options
Medical assistant training costs in France vary significantly based on institution type, program duration, and certification level. Public vocational schools and regional training centers typically offer more affordable options compared to private institutions. English speakers may encounter additional costs for language preparation courses or bilingual program premiums.
| Program Type | Institution Examples | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Public Vocational Training | Lycées professionnels, GRETA networks | €500 - €2,000 per year |
| Private Career Schools | Specialized healthcare training institutes | €3,000 - €8,000 total program |
| University-Affiliated Programs | IUT programs, university certificates | €1,500 - €4,000 per year |
| International Bilingual Programs | Select private institutions | €5,000 - €12,000 total program |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Program durations typically range from 9 months to 2 years, depending on certification level and prior healthcare experience. Financial aid options, apprenticeship programs combining work and study, and regional funding opportunities may reduce overall costs. English speakers should factor in potential language course expenses and living costs when budgeting for training in France.
Career Prospects and Certification Recognition
Completing medical assistant training in France opens pathways to employment in hospitals, private practices, specialty clinics, and healthcare administrative offices. Certification recognition depends on program accreditation and alignment with French professional standards. The Diplôme d’État level certifications receive broader recognition and facilitate career mobility within France’s healthcare system. English speakers with French medical assistant credentials may find opportunities in international clinics, organizations serving expatriate communities, or facilities requiring bilingual staff. Ongoing professional development and language proficiency enhancement improve long-term career prospects and advancement opportunities within France’s evolving healthcare landscape.
Medical assistant training for English speakers in France requires careful planning, language preparation, and understanding of the French healthcare system’s unique characteristics. Programs provide essential clinical and administrative skills while emphasizing patient-centered care and professional standards. Prospective students should research accredited programs, assess language requirements, and consider financial implications before committing to training. With proper preparation and dedication, English speakers can successfully complete medical assistant training and contribute meaningfully to healthcare delivery in France.




