Daily Tasks and Settings for Carpentry-Related Roles
Some companies may search for individuals able to perform tasks such as cutting, assembling, or measuring materials in support of carpentry routines. These tasks could be done indoors or outdoors, depending on the project. Flexible scheduling, hourly pay, and support like health insurance, paid leave, or structured guidance may be provided. Prior experience is not always required, and career growth possibilities may be available through internal development or mentorship.
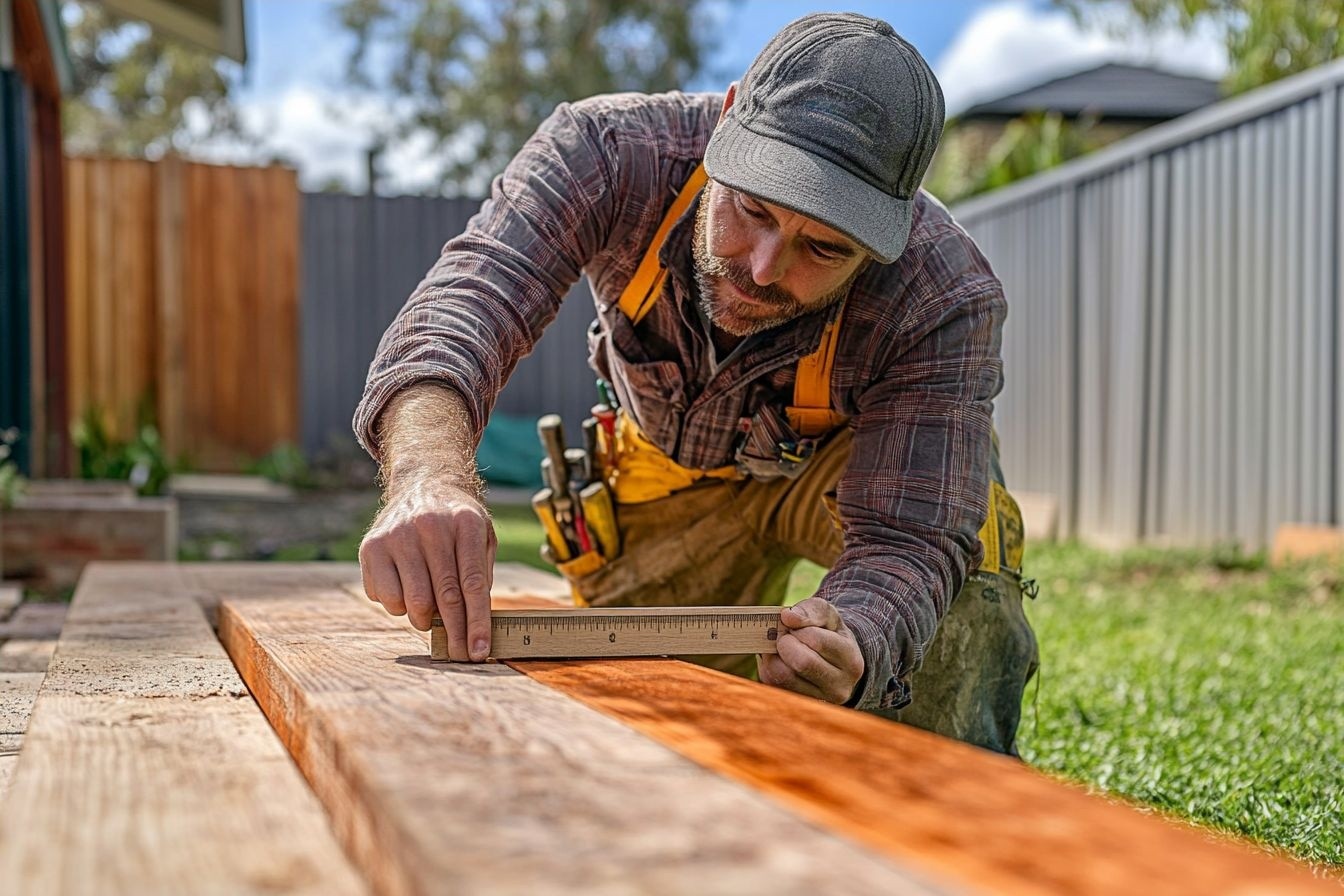

What are the primary responsibilities of a carpenter?
Carpenters are responsible for a wide array of tasks that involve working with wood and other materials to construct, repair, and install various structures and fixtures. Their daily duties often include reading and interpreting blueprints, measuring and cutting materials to precise specifications, and assembling components using a variety of tools and techniques. Carpenters may also be involved in framing walls, installing doors and windows, building staircases, and creating custom cabinetry. Depending on the specific job or project, they might work on everything from rough carpentry for new construction to fine woodworking for interior finishes.
What types of tools are commonly used in carpentry-related settings?
Carpenters rely on a diverse toolkit to perform their daily tasks efficiently and accurately. Hand tools such as hammers, chisels, planes, and saws are staples in any carpenter’s arsenal. Power tools like circular saws, drills, nail guns, and sanders help speed up work and improve precision. Measuring and layout tools, including tape measures, levels, squares, and chalk lines, are essential for ensuring accurate cuts and proper alignment. Additionally, specialized tools for specific tasks, such as routers for creating decorative edges or biscuit joiners for seamless wood joining, are commonly used in carpentry settings.
How is safety ensured during basic construction or assembly tasks?
Safety is paramount in carpentry-related roles due to the potential hazards associated with working with sharp tools, heavy materials, and sometimes at heights. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a crucial component of safety protocols, including safety glasses, hearing protection, work gloves, and steel-toed boots. For tasks involving dust or fumes, respirators may be necessary. Proper training on tool usage and safety procedures is essential, as is maintaining a clean and organized work area to prevent trips and falls. Regular equipment inspections and adherence to workplace safety regulations help minimize risks and ensure a safe working environment for all team members.
What materials are handled in typical carpentry environments?
While wood is the primary material in carpentry, modern carpenters work with a variety of materials to meet diverse project requirements. Common wood types include pine, oak, maple, and cedar, each with unique properties suitable for different applications. Engineered wood products like plywood, medium-density fiberboard (MDF), and oriented strand board (OSB) are frequently used in construction. Carpenters also handle non-wood materials such as laminates, veneers, and composite materials. Additionally, they work with fasteners like nails, screws, and adhesives, as well as hardware components for doors, windows, and cabinetry.
How are team-based carpentry activities usually coordinated?
Carpentry projects, especially larger ones, often require effective teamwork and coordination. Project managers or lead carpenters typically oversee the work, assigning tasks based on individual skills and experience. Daily or weekly team meetings are common to discuss project progress, address challenges, and plan upcoming tasks. Communication tools like two-way radios or mobile apps may be used to facilitate real-time coordination on job sites. Collaborative problem-solving is often necessary when encountering unexpected issues or design changes. Skilled carpenters may also mentor apprentices or less experienced team members, fostering knowledge transfer and skill development within the team.
What career growth opportunities exist in carpentry-related fields?
The carpentry field offers numerous pathways for career advancement and specialization. In the United Kingdom, carpenters can progress from apprentice to journeyman and eventually to master carpenter status. With experience, carpenters may move into supervisory roles such as foreman or project manager, overseeing larger teams and more complex projects. Some carpenters choose to specialize in areas like architectural woodworking, historical restoration, or green building practices, which can lead to niche expertise and higher-paying opportunities. Entrepreneurial carpenters may start their own contracting businesses or custom woodworking shops. Additionally, experienced carpenters can transition into related fields such as building inspection, construction management, or teaching at vocational schools.
Carpentry-related roles offer a dynamic and rewarding career path for those who enjoy working with their hands and seeing tangible results of their efforts. From daily tasks involving precise measurements and skilled craftsmanship to the coordination of team-based projects, carpentry encompasses a wide range of activities that contribute to the creation and maintenance of our built environment. As the construction industry continues to evolve, carpenters who stay updated with new technologies and sustainable building practices will find themselves well-positioned for long-term success and career growth in this essential trade.