Airport Industry in Japan: Operational Environment and Industry Structure
Japan’s airport industry is a complex system that supports transportation, logistics, and passenger services across the country. This article provides general information about airport environments, operational standards, and typical conditions found within airport facilities. The content focuses on industry-level organization and infrastructure rather than specific employment-related topics. Discover more inside.
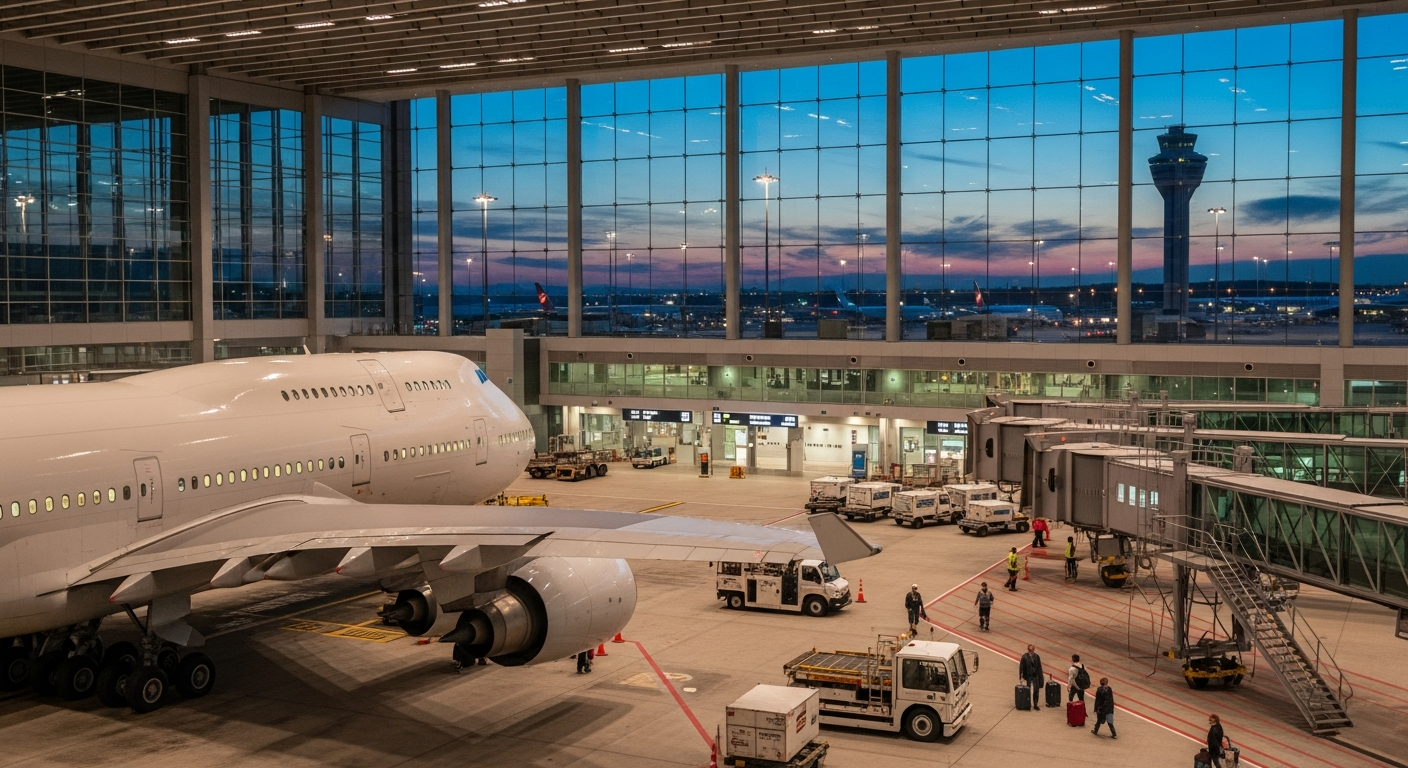

Japan’s airport infrastructure represents one of the most developed aviation networks in Asia, characterized by strategic planning, technological innovation, and operational efficiency. The sector encompasses various facility types, from major international gateways to smaller regional airports that ensure connectivity across the archipelago.
Airport Infrastructure Development in Japan
The Japanese aviation infrastructure has evolved significantly since the post-war era, with systematic expansion and modernization efforts. The network includes three primary international airports: Narita International Airport, Haneda Airport, and Kansai International Airport, which serve as primary gateways for international traffic. These facilities handle the majority of Japan’s international passenger and cargo operations, connecting the country to global destinations across six continents.
Regional airports complement these major hubs, providing essential connectivity to smaller cities and remote areas. Many of these facilities serve dual purposes, accommodating both commercial aviation and supporting emergency services, disaster relief operations, and regional economic development initiatives.
Aviation Infrastructure Management Systems
Japan employs sophisticated management systems to coordinate airport operations across its network. The Civil Aviation Bureau oversees regulatory compliance and safety standards, while individual airport operators manage day-to-day operations. This structure ensures consistent service quality and safety protocols throughout the system.
Technological integration plays a crucial role in operational efficiency. Advanced air traffic management systems, automated baggage handling, and digital passenger processing contribute to smooth operations even during peak travel periods. These systems help maintain Japan’s reputation for punctuality and service quality in aviation services.
Airport Operations and Service Delivery
Operational excellence in Japanese airports stems from comprehensive planning and attention to detail. Ground handling services, passenger processing, and cargo operations follow standardized procedures designed to minimize delays and enhance customer experience. Many facilities incorporate traditional Japanese hospitality principles into their service delivery approach.
Maintenance and safety protocols receive particular emphasis, with regular inspections and preventive maintenance programs ensuring operational reliability. Environmental considerations also influence operational decisions, with many airports implementing sustainable practices and energy-efficient technologies.
Transport Logistics Integration
Japanese airports function as integral components of the broader transport logistics network. Multimodal connectivity allows seamless transfers between air, rail, and road transport systems. Major airports feature direct rail connections to urban centers, reducing travel times and environmental impact.
Cargo operations represent a significant aspect of airport functionality, with dedicated freight facilities supporting Japan’s export-oriented economy. Specialized handling capabilities for various cargo types, including perishables, electronics, and automotive components, support diverse industry requirements.
| Airport Type | Examples | Annual Passengers | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| International Hub | Narita, Haneda, Kansai | 20-80 million | Long-haul routes, cargo facilities |
| Regional Airport | Sendai, Hiroshima, Kagoshima | 1-5 million | Domestic connections, local services |
| Local Airport | Shizuoka, Ibaraki, Komatsu | 100k-1 million | Regional connectivity, charter services |
Industry Structure and Governance
The Japanese airport industry operates under a mixed ownership model, combining government oversight with private sector participation. Major airports have undergone various privatization initiatives, allowing private companies to manage operations while maintaining government involvement in strategic planning and regulation.
This structure promotes efficiency while ensuring public interest considerations remain central to decision-making processes. Private operators bring commercial expertise and innovation, while government oversight maintains safety standards and ensures equitable access to aviation services across different regions.
Regulatory frameworks establish clear guidelines for airport operations, safety protocols, and environmental compliance. These regulations evolve continuously to address changing industry needs, technological developments, and international aviation standards.
Japan’s airport industry continues adapting to changing travel patterns, technological advancements, and economic conditions. The sector’s emphasis on operational excellence, customer service, and systematic planning positions it well for future challenges and opportunities in the global aviation market. Integration with broader transport networks and commitment to sustainable practices further strengthen the industry’s long-term viability and contribution to Japan’s economic development.